Supervisors have a direct impact on employee performance and ultimately on the success of the business. This guide explores the essentials of performance management, including its purpose, benefits, practical training techniques and successful strategies for putting it into action. Following these insights can help leaders boost team performance, foster collaboration and achieve long-term results.
What Is Performance Management Training?
Performance management training is a professional development process designed to help managers, supervisors and HR professionals learn how to effectively evaluate, support and improve employee performance.
Why Is Performance Management Training for Managers Important?
A strong, effective and skilled manager or supervisor wants their employees to do their best, but to make that happen, they need to understand how to support their team, track progress and recommend improvements. Most managers benefit from dedicated training to develop these abilities.
Performance management training helps managers and supervisors align employee goals with organizational objectives while strengthening leadership skills at every level. It also plays a key role in talent retention and helps foster a performance culture supported by communication, collaboration and continuous growth.
8 Benefits of Performance Management Training
Performance management training delivers value not just for employees but also for managers and the organization as a whole. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Helps managers set clear, measurable goals that align with organizational objectives: Training teaches you how to set goals that employees can understand, measure and achieve, ensuring everyone works toward the same outcomes.
2. Improves communication and feedback between supervisors and employees: Training helps you give clear, constructive feedback and encourages open, two-way communication so employees feel supported and understood.
3. Increases employee engagement, motivation and accountability: Investing in performance management training shows that you take your role seriously and are committed to supporting and developing your employees, which can boost motivation and ownership of their work.
4. Builds consistency and equity in performance evaluations: Performance management training helps you apply standards consistently, ensuring that all employees are evaluated equitably and objectively.
5. Identifies skill gaps and development opportunities: Training equips you to give constructive feedback, helping you spot skill gaps and areas where employees can grow or improve.
6. Strengthens leadership and coaching capabilities: You’ll develop the skills to guide, mentor and motivate your teams, improving overall leadership quality.
7. Reduces turnover by fostering a culture of growth and recognition: When you’re equipped to support employee development and recognize achievements, employees are more likely to stay engaged and committed to the organization.
8. Enhances overall productivity and organizational performance: Performance management training equips you to align team efforts with company goals, streamline workflows and maximize results at both the individual and organizational levels.
Common Challenges and Mistakes in Performance Management
Implementing an effective performance management system isn’t always easy. Managers and organizations often face obstacles along the way. Here are some of the most common challenges and mistakes:
- Inconsistent or infrequent manager feedback: Consistency is crucial. When you fail to provide regular check-ins or follow up on SMART goal progress, for example, it sends the message that you don’t value employee performance and development.
- Unclear or misaligned performance expectations: It’s important that everyone is on the same page about goals and expectations, from the top of the organization to managers to their direct reports. When messages are mixed and expectations are unclear, employees may feel confused, frustrated and unsure how to prioritize their work, which can hurt performance and morale.
- Lack of proper training for supervisors on performance management: Effective performance management must be supported by clear process and supervisory skills training for everyone with direct reports. Ideally, the process is universal in an organization so that there can be strong cultural and peer support.
- Inadequate support for employee development and growth opportunities: One of the most important aspects of performance management is supporting employees through guidance, mentorship and opportunities to grow. Failing to do so can lead to disengagement, low morale and higher turnover.
- Poor documentation and follow-up on performance issues: Even with a regular meeting schedule, without clear records and an agenda to go over previous open issues, important details can be lost, and performance problems may go unaddressed.
7 Skills and Competencies for Effective Performance Management
So what does effective performance management actually look like? Let’s break down some of the most important skills and competencies, including hypothetical but real-world examples that illustrate these skills and competencies in action.
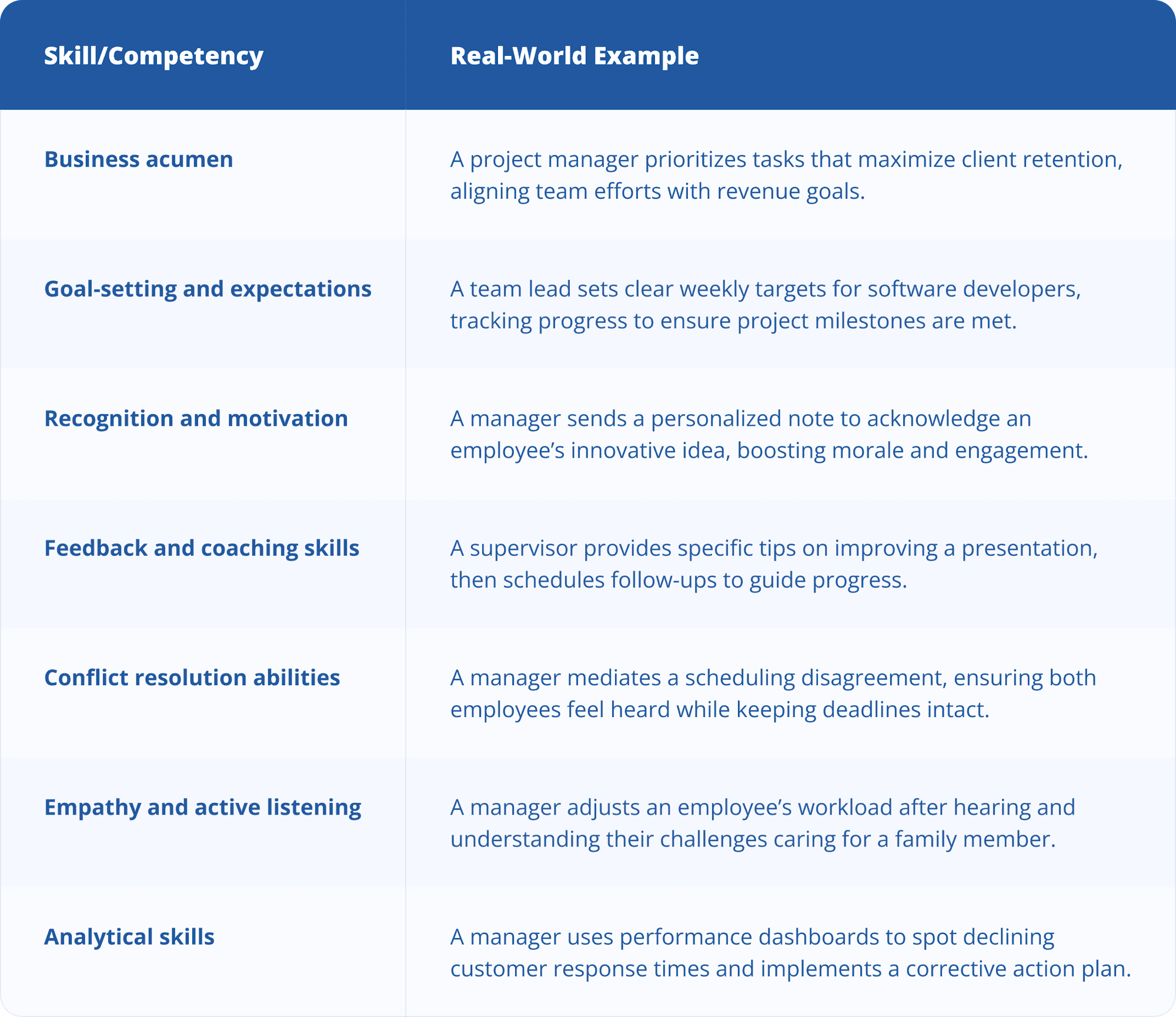
1. Business acumen
It’s important to understand how specific actions or projects impact desired business results. This knowledge is essential for setting appropriate goals, making informed decisions and evaluating performance effectively.
Real-world example:
A marketing manager with strong business acumen recognizes that improving customer response times can increase client satisfaction and retention, both of which are key revenue drivers. Instead of simply tracking the “number of tickets closed,” they align performance goals around metrics that directly contribute to the organization’s success, such as customer satisfaction scores or renewal rates.
2. Goal-setting and expectations
The ability to set specific, measurable goals and clear expectations is the mark of a strong supervisor and the foundation of successful performance management.
Real-world example:
A supervisor on a sales team sets a goal for each employee to increase their quarterly sales by 10%, clearly outlining the steps and resources available to achieve it. By tracking progress and providing feedback regularly, the supervisor ensures employees know what’s expected and can adjust strategies to succeed, improving both individual and team performance.
3. Recognition and motivation
The ability to recognize an employee’s strengths, achievements and improvements is key to retaining talent and boosting morale. Effective supervisors also model motivation, inspiring their teams to perform at their best.
Real-world example:
A manager notices a team member consistently exceeds project deadlines with high-quality work. They publicly acknowledge the achievement in a team meeting and offer a small reward or additional responsibility aligned with the employee’s career goals. This recognition motivates not only the individual but also encourages the entire team to maintain high performance.
4. Feedback and coaching skills
Observing employee performance is only part of a manager’s role. It’s equally important to deliver constructive feedback and provide guidance in a way that promotes growth and improvement.
Real-world example:
A manager notices an employee’s reports are frequently missing key details. Instead of criticizing them in front of the team, the manager schedules a one-on-one session, highlights what’s working well, and offers specific, actionable suggestions for improvement. They also check in regularly to coach the employee on applying the feedback, helping them improve performance while maintaining confidence and engagement.
5. Conflict resolution abilities
Conflict is a natural part of any workplace, and effective managers recognize that how it is handled can directly impact team productivity and morale. Strong conflict resolution abilities involve identifying the root cause of disagreements, actively listening to all parties and facilitating open, respectful communication.
Real-world example:
A manager observed a disagreement between two team members on the approach to a client deliverable. The manager facilitated a meeting to clarify perspectives, find common ground and guide the team toward a compromise, keeping the project on schedule while strengthening team collaboration.
6. Empathy and active listening
Interpersonal skills like empathy allow you to understand employees’ experiences and perspectives. Active listening ensures they truly hear and process what’s being said. Together, these skills build trust, improve communication and strengthen relationships.
Real-world example:
An employee begins missing deadlines after taking on new caregiving responsibilities at home. Instead of assuming poor performance, the manager listens with empathy, learns about the situation and works with the employee to adjust workload and deadlines.
7. Analytical skills
Data plays a role in every aspect of business, including performance management. Managers with strong analytical skills can interpret metrics and identify trends and then use these insights to make informed decisions that promote improvement and support organizational goals.
Here’s a quick reference to the key skills and what they look like in action.
5 Training Techniques and Frameworks for Supervisors
Performance management training doesn’t follow a one-size-fits-all model. Some organizations adopt a single method, while others combine multiple approaches to best meet their needs. The following are some of the most widely used training techniques and frameworks for supervisors.
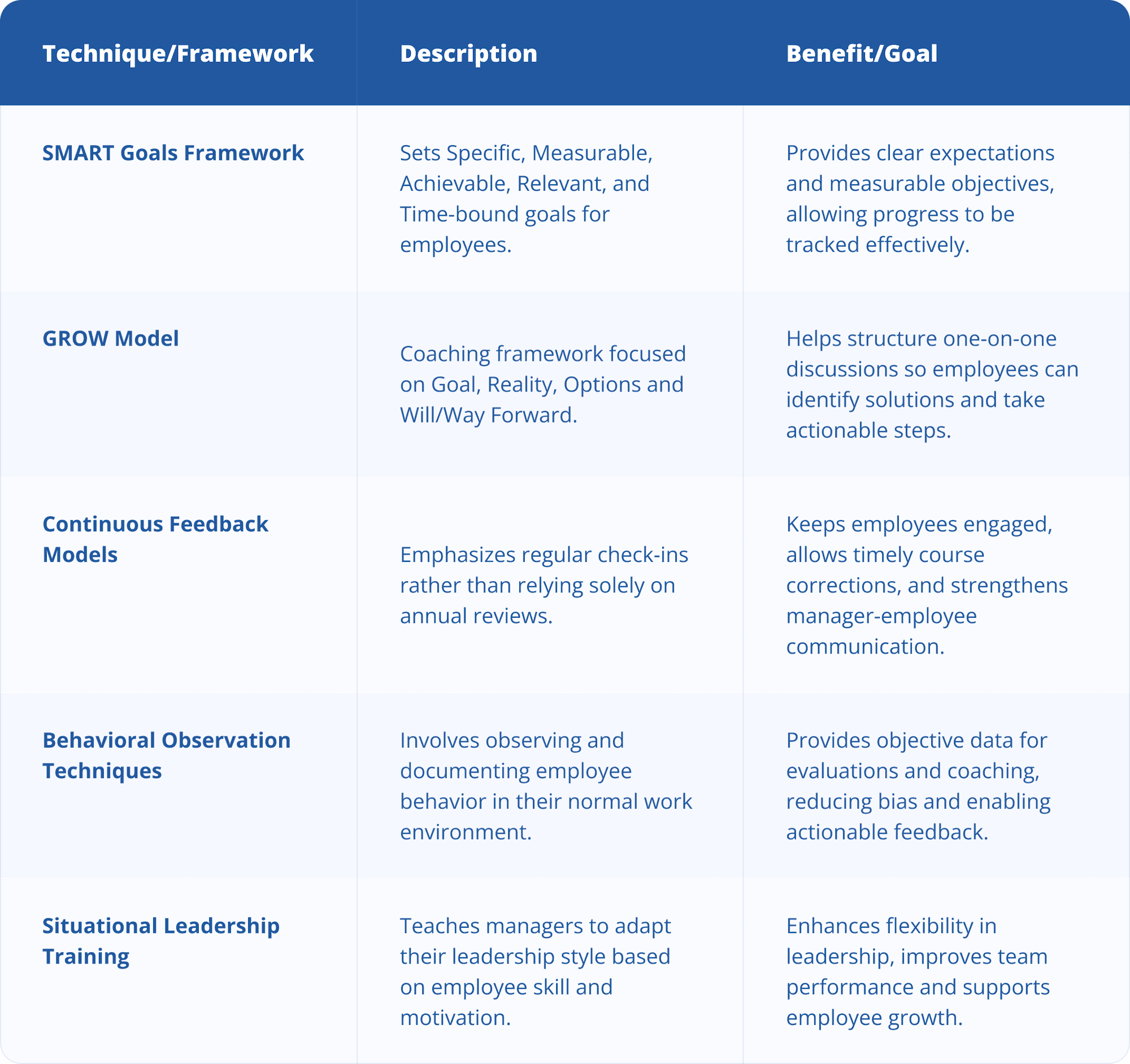
- SMART Goals Framework: This method for setting Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant and Time-bound (SMART) goals helps managers and employees set clear expectations, track progress and achieve measurable results. SMART goals provide specificity and give employees concrete objectives to work toward, while allowing employers to monitor progress, which is something often missing from generic goals. This approach is especially common in organizations that prioritize performance management and professional development.
- The GROW Model: This is a coaching framework that stands for Goal, Reality, Options and Will/Way Forward. It’s often used in one-on-one coaching or performance discussions and enables managers to structure conversations in a way that helps employees identify solutions and take actionable steps.
- Continuous Feedback Models: This approach emphasizes regular performance discussions rather than relying solely on annual reviews. Managers and supervisors often integrate these check-ins into weekly or monthly meetings, which keeps employees engaged, enables timely course corrections and strengthens manager-employee communication through consistent, frequent interactions.
- Behavioral Observation Techniques: This method involves observing and documenting employee behavior to inform evaluations and coaching. It’s typically used as needed, often before performance reviews or coaching sessions. By observing employees in their normal work environment, managers can gather objective data on how an employee works and behaves. This provides concrete opportunities for feedback, reduces bias and helps managers give actionable guidance, making coaching and development more effective.
- Situational Leadership Training: This approach teaches managers to adjust their leadership style based on the skill and motivation of each employee. This type of training is often applied during team projects or when managing new or changing roles. This also equips managers with the ability to lead more flexibly, improving both team performance and employee growth.
To help you see how these approaches differ, and what they achieve, refer to this quick comparison chart.
5 Tips for Implementing and Sustaining Performance Management Improvements
Enhancing performance management starts with practical steps that support both managers and employees. Successful initiatives combine clear strategies, the right tools and ongoing attention to maintain consistent performance and growth. Here are some helpful considerations to keep in mind.
1. Leverage performance management software.
Tools can streamline goal tracking, feedback and performance reviews, making it easier for you to monitor progress and stay organized.
2. Hold regular review meetings.
Consistency is key. Regular check-ins with employees ensure that progress toward goals is monitored, challenges are addressed promptly and feedback is shared in a timely manner. These meetings help keep employees engaged and aligned with organizational objectives.
3. Implement employee self-evaluations.
Performance management is a two-way street. While manager and supervisor feedback is important, self-evaluations give employees a voice in the process. It’s a way for employees to think about what’s working and what isn’t, take ownership of their goals and reflect on challenges or areas of growth.
4. Link rewards and development opportunities to employee performance.
Recognizing and rewarding strong performance reinforces desired behaviors and motivates continued improvement. Consider setting up a system in which achievements lead to tangible outcomes such as bonuses, promotions or professional development opportunities.
5. Participate in ongoing supervisor training.
Effective performance management requires skilled leaders. Ongoing training helps supervisors strengthen their coaching, communication and feedback abilities. Consider partnering with an organization that specializes in training and can tailor a program to your specific goals and needs. Additionally, instructor-led training provides opportunities for real-time guidance, interactive learning and practice of techniques that can be immediately applied in the workplace.
At Global Partners Training, we design service-focused, interactive, industry-specific training programs that drive real behavior change and business results. Whether the goal is developing service leadership, achieving service excellence or strengthening customer relationship skills, our approach combines deep subject matter expertise, flexible delivery formats and measurable outcomes.
For more insights on fostering positive employee performance and a healthy workplace, download our eBook: Transforming Negative Workplace Behavior: 5 Effective Strategies for Leaders.